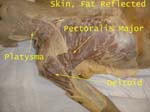
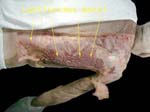
Superficial Muscles
Platysma is a muscle of facial expression
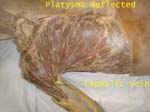
Cephalic vein located in the groove between deltoid and pectoralis major is used for catheterization
Lymph nodes in axilla vary in number as well as size
Serratus so called because of its edges, arises from ribs
Lattisimus has a very wide origin but a very narrow insertion
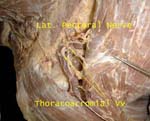
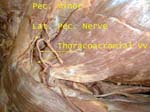
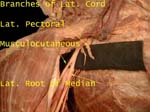
Lateral Pectoral Nerve
Named based on origin from lateral cord, supplies pectoralis major
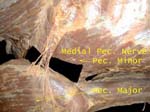
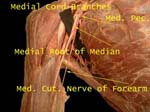
Medial Pectoral Nerve
Is so called as arises from medial cord but is lateral to the lateral pectoral nerve, supplies both pectoral muscles
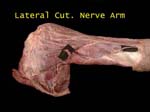
Medial Cutaneous Nerve of Arm
From medial cord, size directly proportional to intercostobrachial nerve as both share in supply of skin on medial side of arm
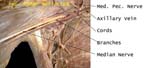
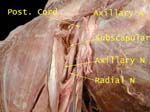
Brachial Plexus and Axillary Vein
Cords named in relation to 2nd part of axillary artery, vein is medial
Lateral Pectoral Nerve
Lateral pectoral nerve accompanied by thoracoacromial vessels pierces the fascia between clavicle and pectoralis minor (clavipectoral fascia)
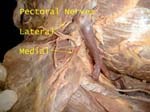
Pectoral Nerves
Note their position, named according to their origin from the cords
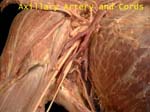
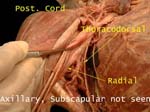
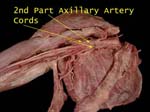
Axillary Artery and Cords
Cords hug the part of the axillary artery that is deep to pectoralis minor (2nd part)
Lateral Cord of Brachial Plexus
(Formed by anterior divisions of upper and middle trunk) Has three branches
Musculocutaneous supplies muscles (flexors) in arm and skin in forearm (lateral side)
Medial Cord of Brachial Plexus
(Formed by anterior division of lower trunk) Has five branches
Median nerve is formed by roots from lateral as well as medial cords
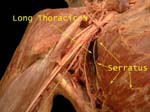
Long Thoracic Nerve
So called as starts in neck (directly from roots C5-7) and goes down thorax supplying digitations of serratus anterior, if destroyed results in winged scapula
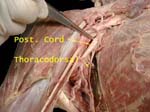
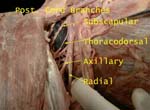
Posterior Cord of Brachial Plexus
Gets contribution from each trunk of brachial plexus, has five branches
Axillary nerve winds around the neck of humerus, can be damaged here, resulting in inability to abduct arm and sensory loss in badge area
What effect on lateral rotation?
Radial nerve supplies most of structures in posterior arm, forearm and hand
Thoracodorsal nerve accompanied by similarly named artery on way to supply lattissimus dorsi, at risk of damage during axillary lymph node dissection in breast cancer surgery
Generally two subscapular nerves, supply teres major in addition to subscapularis
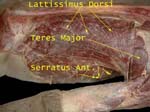
Latissimus Dorsi
Note its wide origin from iliac crest, lumbar fascia and thoracic vertebrae
Note how it winds around the teres major, sometimes it gets a slip from inferior angle of scapula
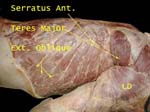
Here the lattisimus has been reflected to expose the interdigitating fibers of serratus and external oblique
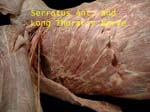
Serratus Anterior and Long Thoracic
Digitations of serratus cut close to its origin, nerve lying on its surface
Serratus Anterior off Chest Wall
Upper limb has been removed by cutting the clavicle (only bony connection between the upper limb and the chest wall), other muscles, axillary vessels and nerves
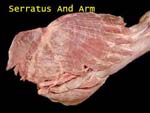
Serratus Anterior and Arm
Remember its action?
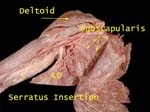
Serratus Anterior Insertion
It is inserted on medial border, costal surface of scapula. As more fibers are inserted into the inferior angle, it rotates the scapula thus helping abduct arm above 90 degrees
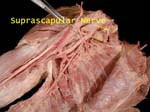
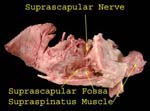
Suprascapular Nerve
Contains C5 -6 fibers as comes of the upper trunk.
Cords and Axillary Artery
Cords are named according to their relation to this part of the axillary artery
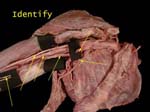
Identify
From right to left of image these are: medial pectoral, thoracodorsal, ulnar, axillary artery, median, and medial cutaneous nerve of arm and forearm
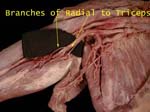
Radial Nerve - Branches to Triceps
Note that branches are given off in axilla even though the nerve traverses the spiral groove of humerus between the heads of triceps. Hence in midshaft fracture of humerus damaging radial nerve, all of triceps is not denervated
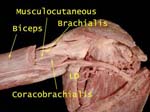
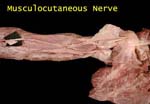
Musculocutaneous Nerve
It pierces coracobrachialis, lies between biceps and brachialis and supplies all three
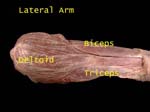
Muscles - Lateral Arm
Three muscles supplied by three different nerves
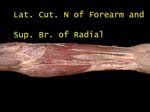
Lateral Cutaneous Nerve Arm
There are two small nerves, upper is a branch of axillary and lower is from radial
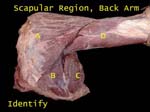
Identify (Scapular Region)
Answers
ABCD start with DITT
A = Deltoid, B = Infraspinatus, C = Teres Major, D = Triceps
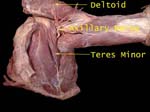
Axillary Nerve
Winds around humeral neck and supplies two muscles – deltoid and teres minor
Is accompanied by posterior circumflex humeral artery
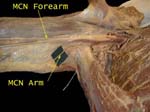
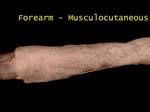
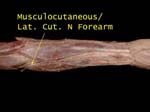
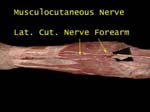
Forearm - Musculocutaneous 1
It supplies skin on lateral part of forearm and is often called lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm
Muscles in arm and skin in forearm!
The nerve emerges on lateral side of elbow, partly hidden by fat and fascia
Nerve is exposed, also note median cubital vein
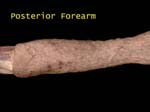
Posterior Forearm
What would you call the nerve that supplies skin of posterior forearm?
Relecting skin exposes some nerves and vessels
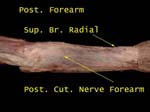
Posterior cutaneous nerve is a branch of radial (given in the spiral groove)
Superficial branch of radial is on its way to supply back of hand
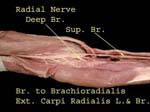
Radial Superficial Branch
At elbow radial divides into two branches, superficial and deep
Superficial branch lies deep to brachieoradialis while lateral cutaneous lies on the muscle
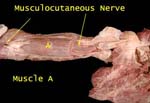
Musculocutaneous Nerve
In arm it lies on brachialis deep to muscle A (biceps)
At elbow emerges on lateral side of biceps tendon
Biceps reflected to display nerve in arm
Lies on brachioradialis in forearm, does not enter the hand
Radial Artery and Nerve
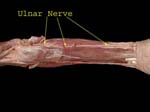
Ulnar Nerve
Forearm
(No branches in arm, can be damaged where it lies behind medial epicondyle) Pierces flexor carpi ulnaris, supplies it and lies on flexor digitorum profundus and supplies ulnar half of FDP
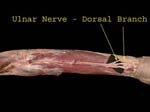
Dorsal
Is given off in distal forearm, winds around ulna to enter dorsal surface of hand
Supplies medial part of dorsum of hand and dorsal aspect of 1 ½ fingers except nail beds (nailbeds by nerves that supply the palmer surface)
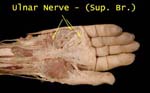
Superficial
Ulnar enters hand accompanied by ulnar artery (nerve is medial to artery) and divides into two
Gives branches to supply skin of medial side of palm and medial 1 ½ fingers
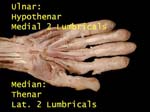
Hypothenar Muscles
Ulnar supplies hypothenar muscles and medial two lumbricals
Median supplies thenar muscles and lateral two lumbricals
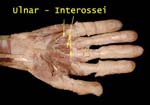
Interossei
All the interossei – three palmar and four dorsal are supplied by the ulnar nreve
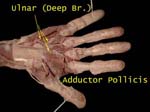
Adductor Pollicis
Supplied by ulnar (not a thenar eminence muscle)
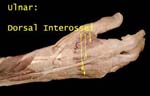
Dorsal Interossei
Supplied by ulnar rneve
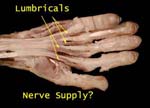
Lumbricals
Medial two by ulnar and lateral two by median (in keeping with parent muscle(medial half of FDP by ulnar and lateral half by median nerve)
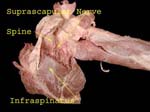
Suprascapular Nerve
After supplying supraspinatus goes around spinoglenoid notch to supply infraspinatus (accompanied by suprascapular artery – important in scapular anastomosis)
Nerve goes through the suprascapular notch to supply the supraspinatus
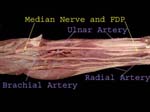
Median Nerve
Elbow
Median nerve is medial to the brachial artery – it is most medial structure in ‘TAN’ (tendon, artery, nerve) Need to remember specially when withdrawing blood from brachial artery
FDP
Superficial muscles have been cut
Median nerve is lying on FDP
Brachial artery bifurcates into ulnar and radial
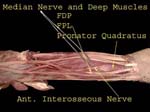
Deep Muscles
Flexor pollicis longus, lateral half of flexor digitorum profundus and pronator quadratus are all innervated by medial nerve branch (anterior interosseous nerve)
Hand
Skin over thenar eminence by median and hypothenar eminence by ulnar
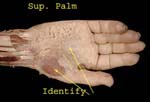
Superficial Palm
Reflecting the skin exposes fat, palmar aponeurosis and abductor pollicis brevis
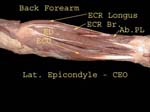
Radial Nerve
Forearm
Radial supplies all muscles in back of forearm
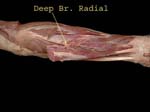
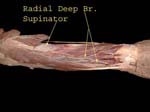
Deep branch of radial is seen piercing supinator muscle
After going in the spiral groove, it emerges between the brachialis and brchieoradialis, gives branches to many of the extensors and then divides into two, deep branch is seen piercing the supinator, superficial branch is mainly sensory
Here the deep branch is seen coming through supinator, it supplies the deep forearm muscles and is often called the posterior interosseous nerve
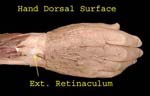
Hand Dorsal Surface
Note the extensor retinaculum
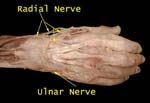
What nerves carry sensations from dorsal surface of hand?
Reflecting skin exposes radial and ulnar nerves as well as some vessels
Arrows indicate areas supplied by each nerve
Here the nerves have been further cleaned and vessels removed