Carpal Bones
Arranged in two rows. Scaphoid is boat shaped and in proximal row. Trapezium is on the side of the thumb (um and thumb go together).

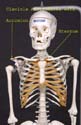
Clavicle
It articulates with the sternum and the acromion. It provides the only bony connection between the upper limb and the axial skeleton.
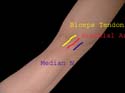
Cubital Fossa
TAN is the order of structures from lateral to medial. Median nerve is the medial most. Keep in mind while taking arterial samples.
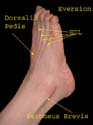
Dorsum of Foot
Extensor digitorum longus tendons go to lateral four toes. Dorsalis pedis artery is medial to Extensor digitorum tendon. Peroneus tendons cross posterior to lateral malleolus. (Remember for working out actions.)
Extensor Tendons in Hand
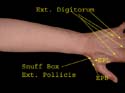
Note the tendons of extensor digitorum to the four fingers. These tendons are interconnected thus making it harder to extend just the middle or ring finger. Extensor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis form the boundary of the snuff box. Radial artery lies in its floor and superficial radial nerve branches cross it.
Flexor tendons at wrist
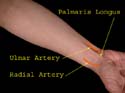
Flexor carpi ulnaris can be easily felt by flexing the wrist against resistance. It is the medial most tendon. Another tendon shown but not labeled here is that of palmaris longus. Remember this muscle is absent in 10% of the population. It comes into prominence by opposing thumb to little finger and flexing the wrist.

Great Saphennous Vein
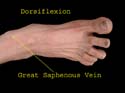
This vein begins from the medial side of the dorsal venous arch and is located in front of the medial malleolus. It is easily accessible here even in very obese or very young individuals – a fact which comes in handy when transfusion is urgently required. Also note the tendon of extensor hallucis longus.
Radial nerve at elbow
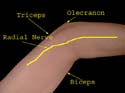
The position of the radial nerve is indicated. After traversing the spiral groove of the humerus, the nerve appears on the lateral side of the arm between brachialis and brachioradialis. It then divides into two, the superficial branch continuing as indicated while the deep branch pierces the supinator.
Arteries at Wrist
The pulsations of radial as well as ulnar arteries at wrist are easily felt. Sometimes pulsations of the ulnar may not be felt as it may be obscured by overlying tissues.
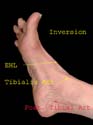
Inverted Foot
The tendon of tibialis anterior becomes prominent as the foot is inverted. The other muscle inverting the foot is tibialis postrerior. The posterior tibial artery pulse is felt a finger’s breadth below and behind the medial malleolus.